5.- Water cycle
|
LISTEN AND READ
|
| Every human, plant, and animal depends on water for survival. Let's explore the Earth's water cycle; what exactly is it? |
 |
|
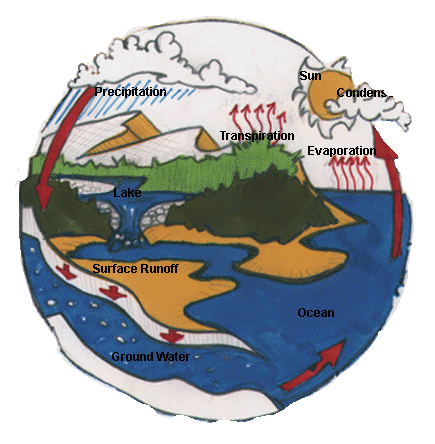
The water
cycle is the way the Earth uses and recycles water. It's
controlled by the sun, which produces energy in the form of heat. This
heat energy causes the water in the world's oceans, lakes, and even
puddles in your backyard to warm and evaporate.
When water is heated, it changes from a liquid to a
gas. This gas is called water vapour, and the process is called evaporation.
When plants give off water vapour, it's called transpiration.
When water evaporates, it rises into the cooler air, collects, and
forms clouds. There, the water vapour
molecules cool down and change back into liquid water.
This is called condensation.
As more and
more water vapour cools into the clouds, the water
droplets that form the clouds become larger and larger. These droplets
get so big that the swirling winds in the atmosphere can no longer hold
them up. The droplets fall from the sky. Precipitation
is the term for the falling, condensed water molecules, which come down
as rain, snow, sleet, or hail-- depending on conditions in the
atmosphere.
When water falls to the Earth, the water seeps
into the soil because of the force of gravity. This seeping is called infiltration.
Or the water flows over the land and into bodies of water, such as
rivers and lakes. Most of this precipitation falls in either coastal
areas or in elevations high up in the mountains. Some of the water that
falls in high elevations becomes run-off water, which is water that
runs over the ground to lower elevations and forms rivers, lakes, and
valleys. Sometimes this water collects
nutrients from the soil it runs over, making the valley good for plant
growth. |
 |
|
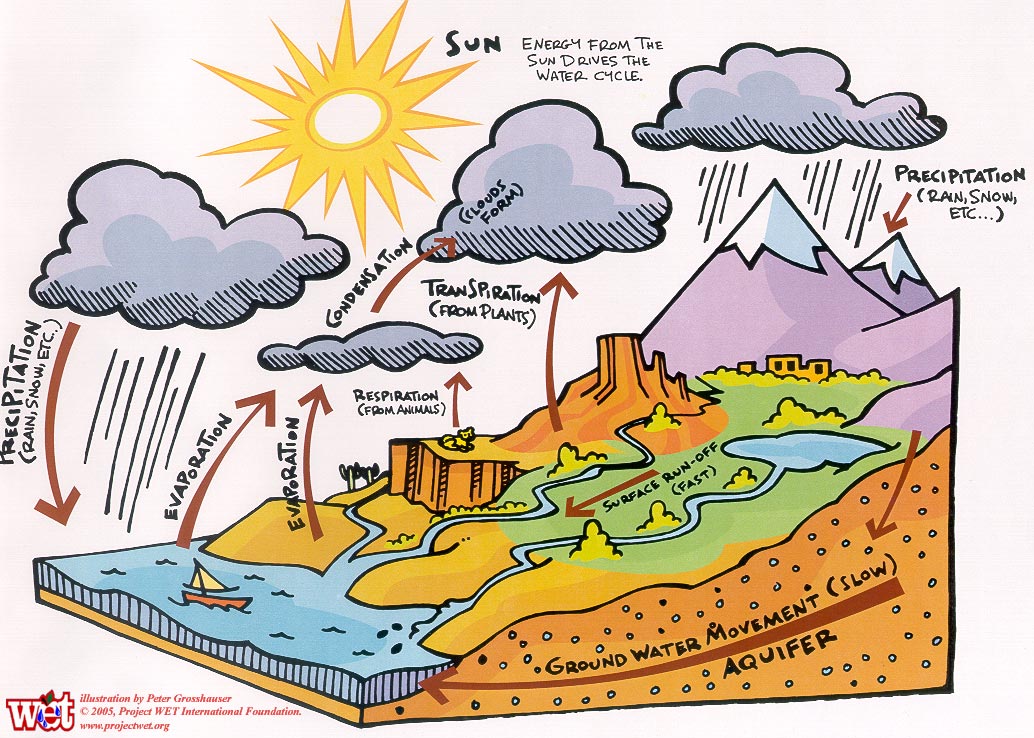
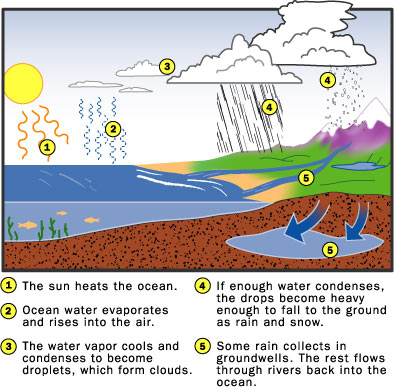
The water
cycle is a process that is constantly recycling
the Earth's supply of water. This is important because humans, animals,
and plants all need water to survive. To review, let's go through the
water cycle step by step: a. First the
water from the Earth's surface evaporates. Then it rises into the
atmosphere, is cooled, condenses, and forms clouds. b. When
enough water collects in the clouds, they release moisture in the form
of rain, sleet, snow, or hail. And once again, the water returns to the
Earth. c. The water
that's fallen to the Earth runs off into lakes, rivers, streams, and
any other body of water. This water will eventually seep through layers
of the Earth's surface where impurities filter out. |
 |
This site is under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 2.5 License
Created by Yolanda Marcos