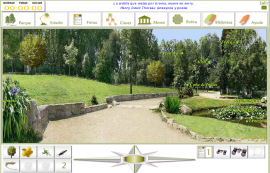
Explore the virtual park in:
http://concurso.cnice.mec.es/cnice2006/material033/,
position the mouse over the cross and move in the direction you want
You can also zoom in and out on the image with the controls on the right:
Click on the 7 enigmas in the squares at the bottom left hand side of the screen. They will help you to find some animals
and plants.
As your explore, make a list on the digital board of the animate and inanimate objects you find.
Remember also the elements which cannot be seen but could be there. What do you imagine we could see on the ground with a
magnifying glass? Could there be other living things? What’s the temperature in the park? Is it dry or humid? Is it the same
if it rains a lot or a little?
Are all the elements on your list living things? Have you included any elements without life?
Watch this video which will explain the biotic and abiotic components. Then classify your list.
BIOTIC AND ABIOTIC FACTORS
Source: http://www.tubechop.com/watch/103988
THE RELATIONSHIPS
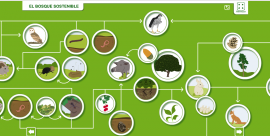
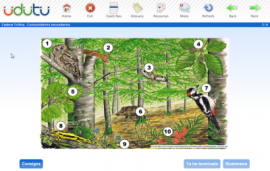
Look at the image:
Source: http://www.ambientech.org/activitats/castella/la_tierra/el_bosque/bosque.html
Living things in a forest do not live in isolation but form relationships with one another. One type of
relationship established between living things is according to food. To survive, each living thing eats something: some eat
plants others eat animals. This relationship is called ‘ the food chain. Depending on what it eats, each living thing
is grouped at a different level. Let’s see:
| Producers: usually plants and some bacteria, which only need light, water carbon dioxide and minerals
to live. They do not eat other organisms, this is why they are called ‘producers’.
|
| Primary consumers : which eat plants and are called herbivores. For example: horses, cows, rabbits.
|
| Secondary consumers: which eat herbivores. They are called carnivores. Some also eat plants. For example,
foxes, wild pigs and others.
|
| Tertiary consumers: which eat herbivores and carnivores. For example, golden eagles, lynx, etc.
|
To understand who eats who the food chain can be represented in a diagram. It begins with what is eaten
and continues to what eats it. For example:
In the animal world , the food chain is often described as a predator-prey relationship, as there is always somethingwhich
eats another thing.
In the next presentation, you can see the relationships of living beings during one day in a forest.
Source: http://www.ambientech.org/activitats/castella/la_tierra/el_bosque/bosque.html
Revise the concept of the food chain with this exercise:
Go to the activity
You have seen the relationship between living things, but what about the non-living elements such as light,
water, the soil, the temperature? What is their function in an ecosystem? Is there a relationship between the biotic and abiotic
factors? And also between the abiotic factors? Think for example, some animals need light to be able to hunt their prey. Others,
like amphibians, need heat to regulate their body temperature. Plants need sunlight for photosynthesis and extract minerals
from the soil. Fish need water to live, but all other living organisms also need water to survive.
Do this next exercise to help you think about other relationships: Relate
Look back at the list you made on the digital board. Can you see some relationships between the biotic
and abiotic elements? Think about the relationships between biotic elements and also with abiotic components.
DEFINITIONS OF AN ECOSYSTEM
Here are some definitions of an ecosystem to help you understand:
- An ecosystem is a group of biotic and abiotic factors and all the relationships between them.
- An ecosystem is a group of living things (animals and plants) and non-living things (environment, air, water,) which
interact with each other.
- An ecosystem is a community of living things in a natural area and the relationships formed between them and the environment
where they live.
- An ecosystem is formed by inanimate or non-biotic elements,( water, minerals, sunlight, climate, etc.) and animate or
biotic elements, (plants, animals, bacteria, algae, etc. It is the relationships and flow of energy between these elements
in a given environment.
You can see that different words are used. Do all the definitions mean the same thing? Re-read them and
compare. See if all the definitions contain the main concepts of an ecosystem: BIOTIC FACTORS, ABIOTIC FACTORS, RELATIONSHIPS.
Which words are synonyms?