Activity 3
Methods of separating homogenous mixtures: evaporation and distillation
Watch the following video to find out about evaporation:
Click on the option Evaporation and watch what happens.
Did you pay attention? It explained the method of separating homogeneous mixtures, called evaporation
which consists of taking advantage of one of the characteristics of liquids. When liquids are heated and reach boiling
point they convert to vapour. So, when the temperature of a mixture of a liquid and a solid is increased, (in the video it
is water and sugar), the water evaporates but the sugar stays in the recipient.
When all the liquid has evaporated, you can obtain sugar again. In this way the two components of the mixture
are separated.
The method of evaporation of the liquid component of a mixture allows us to obtain solids.
Although it may seem complicated, this process happens in your homes when you prepare soup and eat it over
a few days. What happens to the flavour of the soup each time you heat it? Have you noticed that it is tastier or more salty?
This happens because each time the soup is heated, the liquid evaporates and the salt and other ingredients remain. For this
reason, the soup becomes tastier, saltier and thicker.
If you continue to evaporate the water, in the end you will be left with the salt and other solids that
make up the soup, (pasta, vegetables, etc.) The same happened to the sugar in the animation.
Now think: what would happen if you didn’t heat the liquid? Could it evaporate anyway? If you want to find
out, do this simple experiment :
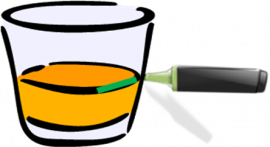
Fill a glass half full of water. Using a permanent marker, indicate the water level. Leave the water at
ambient temperature (in a place in the kitchen).
After a few days, see if the water level coincides with the mark you made. Yes or no? What do you think has happened?
This is also evaporation! Maybe you thought that evaporation only happens when water boils. Well no, not always!
Boiling is a phenomenon that occurs to all the mass of water when
heat is applied and reaches 100ºC. Boiling increases the speed of evaporation, so the process is accelerated when liquid is
heated.
Evaporation occurs on the surface of liquid and can happen at room temperature. How fast
can evaporation occur? This depends on the container and the surface area of evaporation. The larger the surface area, the
faster the evaporation.
To check this, you can do a simple experiment. Place two containers, one with a narrow surface area, like
a glass and one with a wide surface area, like a plate or a dish. Mark the water level on both containers.
Observe them daily and register the changes.
.
Now that we understand evaporation. What would happen if instead of keeping the soild part, we wanted to
obtain the liquid? We would have to recuperate the vapour!
A method to do this is distillation.
Let’s see what this consists of.
In what cases can we apply the method of distillation?
This method is useful to separate the liquid component from the solid one, for example, water and salt.
Distillation is also used to separate a solution of two liquids which boil at different temperatures, like water and alcohol.
Ancient alchemist in his laboratory.
Distillation, like many useful practices in chemistry, owes its invention to the alchemists.
Schemes like this, explain that the process has existed since 300 A.D.
Source: http://saberparacomerlosdestilados.blogspot.com/
2008/05/historia-de-la-destilacion.html
How does distillation work?
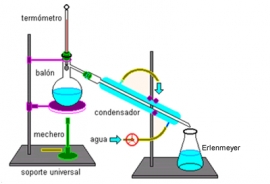
A simple distillation device
In the case of a solution of water and a solute, the mixture is placed in a fire resistant container.
In the image you can see a round distilling flask over a heat source. On heating the mixture, the water
evaporates but the solute doesn’t, just as you have seen in the animation of evaporation: http://portal.perueduca.edu.pe/modulos/m_soluciones/laboratorio_hidratantes2.swf
In distillation, instead of letting the vapour escape into the air, it is cooled in the apparatus called
the,condenser, consisting of two tubes, one inside the other. Water vapour passes through the inner tube and cold water
circulates through the outer tube. As it cools, the vapour condenses and transforms to water which is collected in another
recipient. Like this, the mixture can be separated and the liquid (water) component obtained. The solid component, (salt)
remains in the original container.
Image adapted fromhttp://fraymachete-fq.blogspot.com/
2008/11/destilacin-simple_13.html
Before going on to the final activity, consult other separation methods in this
presentation
Separación de mezclas and complete the following activity: Match.